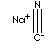| SODIUM CYANIDE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 143-33-9 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 205-599-4 | |
| FORMULA | NaCN | |
| MOL WT. | 49.01 | |
| H.S. CODE | 2837.11 | |
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 6440 ug/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | Hydrocyanic acid, sodium salt; Cyanogran; Cyanobrik; | |
| Kyanid Sodny (Czech); Prussiate of Soda; Cianuro Di Sodio (Italian); Cyanure De Sodium (French); Cyanogran; Natriumcyanid (Dutch); Cianuro de sodio (Spanish); | ||
| SMILES | hydrogen cyanide in caustic soda or liquid soda ash | |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white deliquescent solid | |
| MELTING POINT | 563 C | |
| BOILING POINT | 1496 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.6 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Soluble | |
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
| pH | strong alkaline (aq. solution) | |
| VAPOR DENSITY | 1.7 | |
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 3 Flammability: 0 Reactivity: 1 | |
| FLASH POINT | Not combustible | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS |
||
| Hydrogen cyanide is a highly toxic clear to pale blue liquid or gas with
the odor of bitter almonds. It melts at -14 C and boils at 25.6 C. It is
miscible in water or ethanol and is slightly soluble in ether. Its water
solution, called hydrocyanic acid, is a weak acid. Hydrogen cyanide is mainly
obtained by the reaction of ammonia with carbon
monoxide (Andrussow process) or with natural gas (methane) in the presence of rhodium/platinum catalyst at approximately 1100
C. Very short contact time (milliseconds) is required
to obtain the optimum yield and consequently a high operating temperature is required to reach equilibrium.
It can be
prepared also by the reaction of cyanide salts, e.g., calcium cyanide, with a
strong acid (sulfuric acid). Hydrogen cyanide is obtained as a by-product from
acrylonitrile production. But the portion is small. It is used as a fumigant in
agriculture. The principal use of hydrogen cyanide is in the manufacturing of
acrylates, synthetic fibers (as a starting material for nylon 66), plastics and
cyanide salts, especially sodium cyanide to extract gold from ore. It is used in the manufacturing of organic chemicals; acrylonitrile,
metal
polishes, dyes, rodenticides, pesticides, synthetic fibers, plastics, and
electroplating solutions. Cyanide salts are utilized in metal cleaning, tempering of steel,
gardening, in ore-extracting
processes, dyeing, printing and photography, Electroplating (gold and silver bath), various organic
reactions (Organic
cyanide and nitrile synthesis) manufacture of adiponitril for nylon production. Also used for production of monomers (e.g. acrylates)
as well as in fumigants and pesticides. Sodium
Cyanide is an extremely poisonous white deliquescent
solid; soluble in water and liquid ammonia, and slightly
soluble in ethanol; melting at 563 C, boiling at 1496
C; decomposes rapidly when standing. The aqueous solutions
are strongly alkaline due to salt hydrolysis. This compound
is extremely poisonous due to its reaction with
iron in the blood, so blocking oxygen into the tissues
of the body. It is prepared by absorbing hydrogen cyanide
in caustic soda or liquid soda ash. It is used in extracting
gold- and silver-ores, in electroplating baths, in polishing
metals, in photographic processes, and in fumigating
storage areas, soils and animals. It is also used in
manufacturing chemicals; hydrocyanic acid, other cyanides,
dyes, pigments, nylon intermediates, insecticides and
rodenticides. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
SOLID |
||
|
APPEARANCE |
White Briquette | |
|
NaCN |
98.0% min |
|
| NaOH |
0.5% max |
|
|
Na2CO3 |
1.0% max |
|
|
WATER |
0.5% max |
|
|
30% SOLUTION |
||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear to light yellow liquid |
|
|
NaCN |
30.0% min |
|
| NaOH |
1.5% max |
|
|
Na2CO3 |
1.5% max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 50kgs, 200kgs in iron drum, 1mt in plywood box | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing Group:I) | |
| UN NO. | 1689 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: T+, Risk Phrases: 26/27/28/32, Safety Phrases: 1/2/7/28B/29/45 | ||
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF CYANIDE PROCESS | ||
| Cyanide process, also known as cyanidation, is the most widely used process for extracting gold and silver from ores. The ores are powdered grounds and can be concentrated by flotation. It is then mixed with dilute solutions of sodium (or potassium or calcium) cyanide while air is bubbled through it to form the soluble complex ion, Au(CN)2-1. The precious metals are precipitated from solution by zinc. The precipitates are smelted to remove the zinc and treated with nitric acid to dissolve the silver. | ||